A new artificial intelligence (AI) model called MiniMax-M2 has just made a big splash. For “open” models (ones that researchers and the public can access, unlike closed models like GPT-4), it just set a new all-time high score on a major intelligence test.
But what’s really turning heads is how it’s so smart: it’s incredibly efficient. Think of it as having a giant brain but only using the exact parts it needs for a task, saving a ton of energy.
Here’s a detailed breakdown of what this new AI is, what it’s good at, and the one “catch” you need to know about.
MiniMax-M2 dropped It’s a 230B MoE model that runs like a 10B, thinks like a 200B.
— NearExplains AI (@nearexplains) October 27, 2025
• #1 Open-Source Model: Now ranks #1 on Artificial Analysis benchmarks (#5 overall)
• Built for Agents: Excels at coding, tool use, and test-repair loops
• Deployable: Works with vLLM & SGLang pic.twitter.com/KEELrGmCDt
What Makes M2 So Efficient? The “Sparse” Brain
The most important thing to understand about M2 is its design.
- AI Brains Have “Parameters”: You can think of “parameters” as the knobs, settings, or neurons in an AI’s brain. The more parameters, the more information it can hold and the more complex its “thoughts” can be.
- Total vs. Active Parameters: M2 has a massive 200 billion total parameters. That’s a huge brain. But for any single task, like answering your question, it only uses 10 billion “active” parameters.
This is called “sparsity,” and it’s a huge deal.
Imagine having a giant library (the 200B total parameters) but knowing exactly which 10 books (the 10B active parameters) you need to read to answer a question. You don’t need to read the whole library every time.
Because it only “activates” a small fraction of its brain, M2 is very efficient. This means it’s faster and much cheaper for companies to run, even for lots of people at once. It can run on just a few powerful computer chips (specifically, 4 H100s) instead of needing a giant, custom-built supercomputer.
What is M2 Good At? Being an “Agent”
M2 isn’t just smart at general knowledge; its real talent lies in being an “agent.”
An AI “agent” is one that can do things for you. It’s great at:
- Following Complex Instructions: You can give it a multi-step task, and it will follow through.
- Using Tools: It can be taught to use digital “tools” to find answers, like using a search engine to get new information or a calculator to do math.
This focus on being a helpful assistant is a big trend, especially from Chinese AI labs. They are training their models to be less like chatbots and more like co-pilots that can complete tasks.
The one limitation? M2 is a text-only model. It can’t understand pictures, videos, or sound, unlike some other recent models.
The Catch: Cost vs. Wordiness
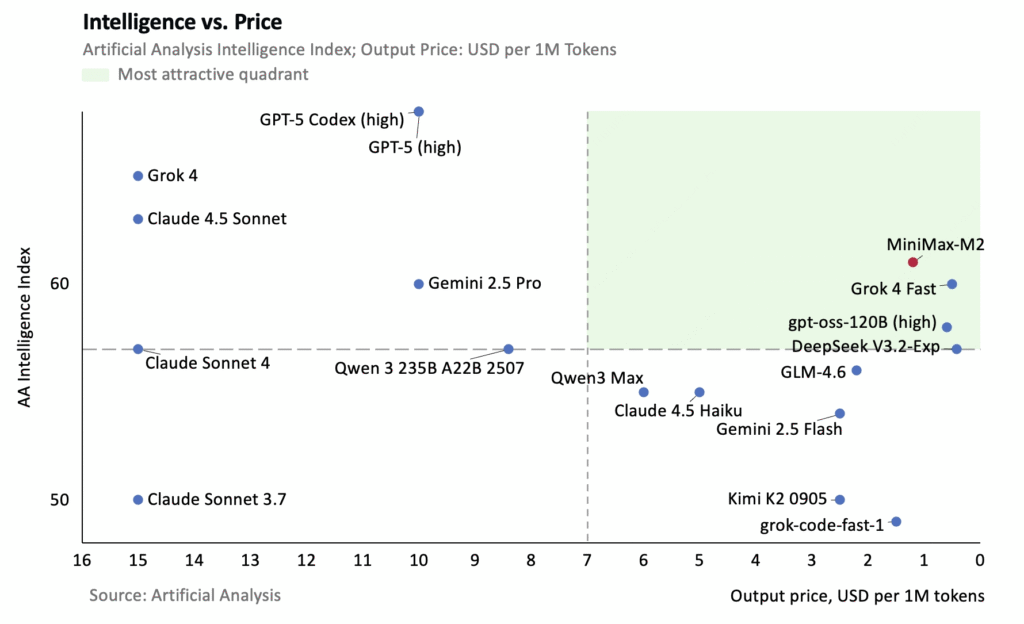
Here’s the “good news, bad news” part.
- The Good News: The price to use M2 is very cheap. It costs only $0.30 (30 cents) to process 1 million “tokens” of input (what you type in) and $1.20 to generate 1 million “tokens” of output (what it writes back). A token is roughly a word or part of a word. This is extremely competitive.
- The Bad News: The model is very “verbose.” This means it’s extremely chatty and uses a lot of words (tokens) to give an answer. In tests, it used as many tokens as Grok 4, another famously wordy model.
So, while the price per word is low, the number of words you pay for is high. This “moderates” the low price, meaning the final cost might not be as cheap as it first looks. It’s a trade-off: you get a highly capable AI, but you also get a lot of extra conversation with it.
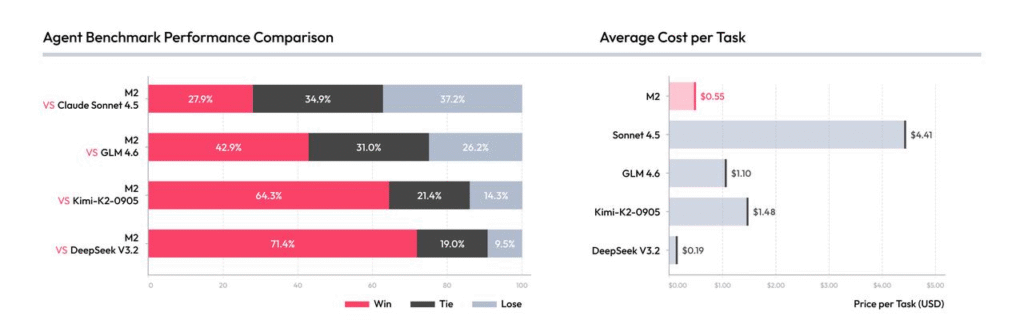
Why This Release Matters
MiniMax-M2 is another major release from a Chinese AI lab, following other powerful models from companies like DeepSeek, Alibaba, and Moonshot AI. This shows a strong trend of leadership and innovation in “open-source” AI coming from China.
In short, MiniMax-M2 is a new record-holder for open AI, showing that a model can be both massive in knowledge (200B parameters) and incredibly efficient to run (10B active parameters). It’s a powerful assistant, but just be prepared for it to be a bit of a talker.
Official Source – MiniMax-M2 Hugging Face Page
Live Test by Codedigipt
